

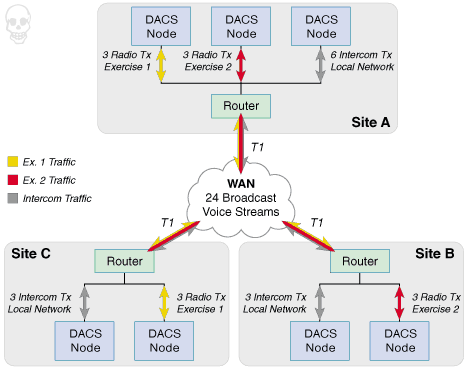
In this scenario, every router connected to the WAN must inspect every voice packet from every operator connected to every DACS processing node.
For example, the router at Site C must examine each Site A intercom voice packet, and then discard it... even though the Site A intercom is for local use only. Then, there's Site B. Site B isn't involved in Exercise 1 at all, but the on-site router has to process each of those voice packets & discard them, too. What a waste of processing power!
Additionally, each T1 pipeline must carry all 24 voice streams. What a waste of bandwidth!
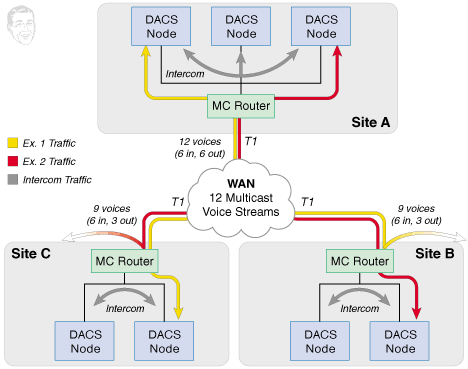
In this scenario, each Multicast Router restricts all intercom traffic to the local network.
Remember Site C? No more Site A intercom voice packets to worry about... they don't even make it that far. Then there's Site B (deja vu). Site B's Multicast Router sends 3 voices to the WAN, and only has to inspect 6 incoming voices (3 for Exercise 1 which are trashed, and 3 for Exercise 2 which are passed through). Talk about light processing load!
Here, the T1 for Site A carries only 12 voices (50% reduction), where the T1s for Sites B & C carry only 9 voices (62.5% reduction). Check out that rockin' bandwidth!